How To Install Bouncycastle Jce Provider
In order to use Oracle JCE Provider, you must install JCE 1.2.1 on your system. I tried installing bouncy castle with osgi:install. Hi, I have a. In this post we will see how to use Bouncy Castle. How to use Bouncy Castle Cryptographic API in NetBeans. There are two ways to install a provider for the JCE.
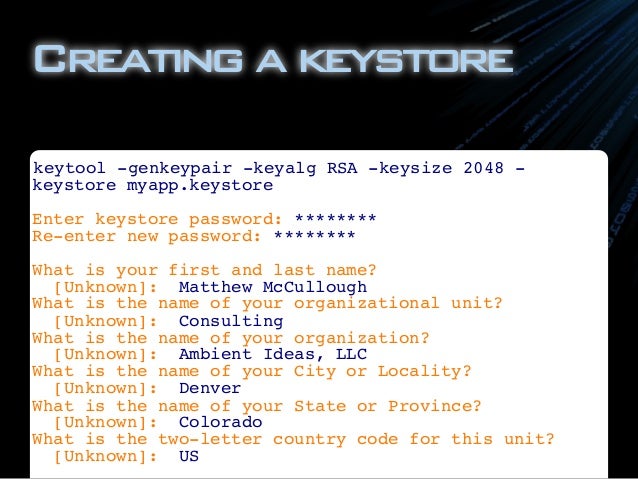
The for Java provides a lightweight cryptography API that works with everything from the J2ME to the JDK 1.6 platform and also a provider for the Java Cryptography Extension JCE (provides an implementation for JCE 1.2.1) and the Java Cryptography Architecture, JCA. Acronis True Image 2013 Bootable Iso Download. The API provides cryptographic functions for Java JDK 1.1 to 1.6 applications and for J2ME (mobile applications) MIDlets.
The API can be downloaded from the. In this post we will see how to use Bouncy Castle Cryptographic API either as a JCA provider or as a lightweight API to develop Java J2SE projects in (works also on older versions). If you want to develop Java applications based on the JSE framework that provide cryptographic services as: • generating hash values to check the integrity of the message or file; • encryption/decryption using symmetric key algorithms; • encryption/decryption using public certificates in a public key infrastructure; • generating message authentication codes for messages; you must use a cryptographic API which provides the necessary classes and methods. The Bouncy Castle API can be used in J2SE applications in two ways: • •; Each approach has its own advantages that are detailed in the next sections. What is the Java Cryptography Architecture (JCA), the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) and the Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) The basic functionality for using cryptographic techniques in Java is provided by the Java Cryptography Architecture (JCA) and its sibling, the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE). The JCA architecture is a provider-based-architecture because it has been defined as an intermediary layer, an interface, between the Java application and the cryptography provider (the actual framework that implements classes for the actual cryptographic algorithms).
Java Cryptography Architecture Overview There are two terms, JCA and JCE, because prior to JDK 1.4 the JCE was an unbundled product. Because now it is included in the JDK, the two terms are used together to describe the same architecture. The Java Cryptography Architecture has been defined as an independent layer. The JCA and the JCE provide a set of classes and interfaces (included in packages such as java.security, javax.crypto, javax.crypto.spec and javax.crypto.interfaces) used by the programmer to communicate with the provider of the actual cryptographic algorithms. That means that the encryption is not done by the JCA, but by the provider. A Java cryptography provider or Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) is Bouncy Castle but it is not the only one.
Pixelmator 2 2 Crack Minds. The Java JDK includes also the standard Sun or SunJCE provider which is included in the JDK and that contains the cryptographic implementations. The JCA architecture represents a simple and common mechanism for adding and using specific providers.
The JCA allows programmers to write once, independently from the used provider. More, the programmer can use multiple providers at the same time or chose one at runtime. This is possible because the JCA was designed around these principles [description from ]: • implementation independence and interoperability because all the providers implement the same collection of interfaces; • algorithm independence and extensibility based on a generic high-level Application Programming Interface (API) used to access the provider. The possibility to plug and use different providers in the JCA is done through the abstract layer that defines a set of factory classes used to generate instances of different engines/algorithms. One of these factory classes is Cipher which encapsulates all the cryptographic algorithms independently from the provider.
For example, the Java syntax is very similar for instantiating a AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) or DES (Data Encryption Standard) engine. Import javax.crypto.*. Deb File Installer Apprentice. //the first configured provider will respond //call the static factory method to create a DES instance Cipher desCipher = Cipher. GetInstance ( 'DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding' ); //call the static factory method to create a AES instance Cipher aesCipher = Cipher. GetInstance ( 'AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding' ); A detailed description of the Java Cryptography Architecture can be found on the page on java.oracle.com.